List of historical sites in Tanzania
List of historical sites in Tanzania -According to the UNESCO World Legacy Convention, which was formed in 1972, the UNESCO World Heritage Sites are locations that are significant in terms of either their cultural or natural heritage. UNESCO stands for the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization. On August 2, 1977, Tanzania became a party to the convention, which made it possible for the country’s historical sites to be considered for inclusion on the list. There are seven UNESCO World Heritage Sites located in Tanzania, and two of them are on the list of World Heritage Sites that are in jeopardy.
The table lists information about each World Heritage Site:
Name: as listed by the World Heritage Committee
Location: province or town of site
Period: time period of significance
UNESCO data: the site’s reference number; the year the site was inscribed on the World Heritage List; the criteria it was listed under. Criteria i through vi are cultural, while vii through x are natural (the column sorts by year added to the list)
Description: brief description of the site
List of historical sites in Tanzania
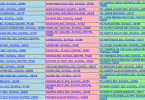
| Name | Image | Location | Period | UNESCO data | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kilimanjaro National Park | Kilimanjaro Region | N/A | 403; 1987; (vii) | The national park holds the Mount Kilimanjaro, the highest point in Africa. The Snow-capped mountain is surrounded by endless plains of savannah. The park also holds numerous large mammals, some of them endangered. | [7] | |
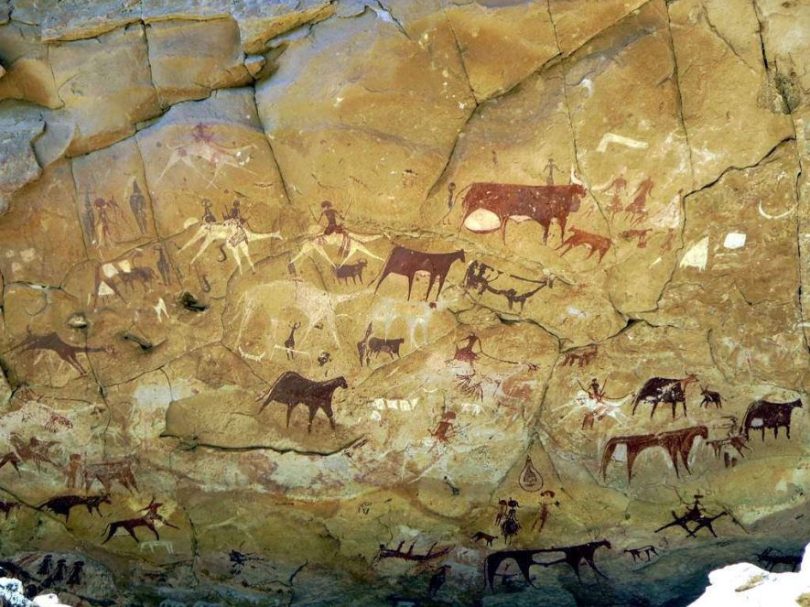
| Kondoa Rock-art sites | Kondoa District | 5th Century | 1183; 2006; (iii),(vi) | The rock-art sites are scattered all over the rift valley and have existed there for over 2000 years. The rock-art provides valuable historical information concerning the evolution of people during the hunter gatherer period. | [9] | |
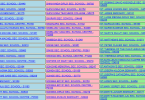
| Ngorongoro Conservation Area | Arusha Region | Modern, 3.6 Million years ago | 39; 1979; (iv),(vii),(viii),(ix),(x) | The Ngorongro Conservation area is a cultural and natural World Heritage Site. The conservation area is home to the Ngorongoro Crater, the world’s largest caldera and the various prehistoric sites. The area also houses various endangered wildlife and the Maasai tribe coexist with the animals. | [3] | |
| Ruins of Kilwa Kisiwani and Ruins of Songo Mnara | Kilwa Kisiwani | 13th to the 16th century | 144; 1981; (iii) | The ruins are of ancient port cities built by Swahili during the 13th century. The ruins are labeled in danger due to the continued deterioration of the property due to natural and human actions. | [4] | |
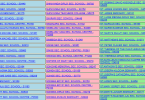
| Selous Game Reserve | Lindi Region, Ruvuma Region & Morogoro Region | N/A | 199; 1982; (ix),(x) | The Selous reserve is 50,000 km2 the size of many foreign countries. The Reserve is home to vast difference in vegetation and large mammals. The site is labeled to be in danger due to the increasing amounts of poaching. | [6] | |
| Serengeti National Park | Arusha Region & Mara Region | N/A | 156; 1981; (vii),(x) | The Serengeti national park is home to one of the largest mammal migration in the world. The annual migration of herbivores and carnivores is one of the most impressive sights in the world. | [5] | |
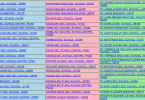
| Stone Town of Zanzibar | Zanzibar City | Arab slave trade period | 173; 2000; (ii),(iii),(vi) | See also: List of Landmarks in Stone TownThe stone town of Zanzibar is a maze of a fusion of multiple cultural influences the town has experienced for centuries. The ancient city still retains Arab, Persian, Indian and Coastal culture. The town is the cultural capital for Swahili Culture. |
In addition to the seven official sites, Tanzania maintains a tentative list of five more sites, provided by Tanzania’s state party.
• Jozani-Chwaka Bay Conservation Area
• Eastern Arc Mountain Forests of Tanzania
• The Central Slave Trade and Ivory Route (trans-national site, includes Bagamoyo, Mamboya, Mpwapwa, Kilimatinde, Kwihara and Ujiji Bagamoyo